Understand, treat, manage & prevent gout.
Understand, treat, manage & prevent gout.
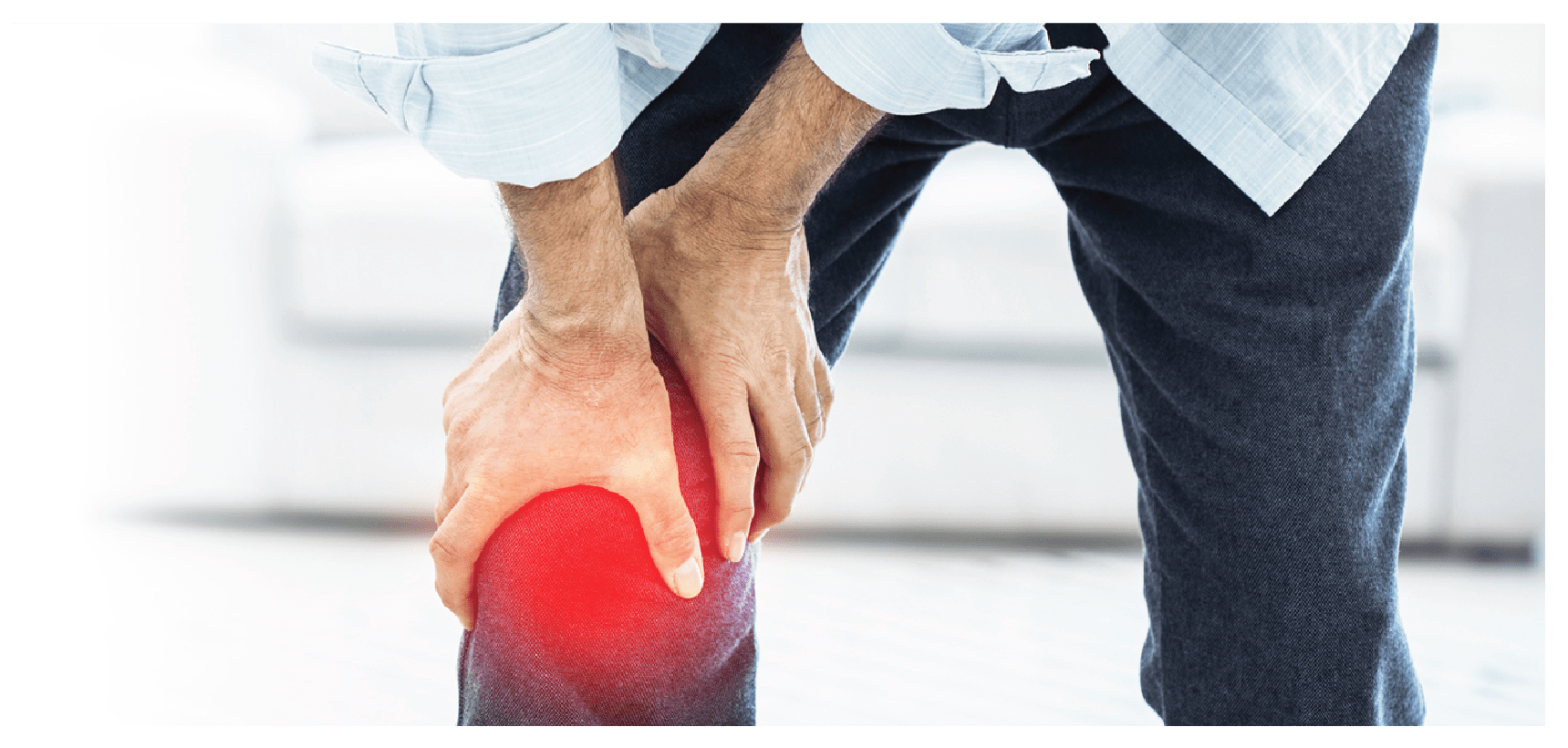

WHAT IS GOUT?
GOUT is a common type of arthritis that develops from deposits of uric acid crystals in the joints. The build-up of these crystals causes attacks of painful inflammation in and around the joints.2
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF GOUT?
When you have GOUT, you can experience GOUT attacks (also called flares) which are sudden episodes of:2
• Sudden onset of severe pain in the affected joint
• swelling
• redness and tenderness
Although GOUT attacks often attack a single joint, such as the big toe, you may also develop a few inflamed joints at the same time. GOUT attacks may be experienced in the foot, ankle, knees, hands or wrists.2,5
When you have GOUT, you can experience GOUT attacks (also called flares) which are sudden episodes of:2
• Sudden onset of severe pain in the affected joint
• swelling
• redness and tenderness
Although GOUT attacks often attack a single joint, such as the big toe, you may also develop a few inflamed joints at the same time. GOUT attacks may be experienced in the foot, ankle, knees, hands or wrists.2,5
WHEN DO ATTACKS HAPPEN AND HOW LONG DO THEY LAST?
Attacks often start overnight and in the early morning without warning however, they can occur at any time. The pain and inflammation usually reach their peak intensity within 12 to 24 hours and generally resolve completely within a few days to several weeks if you do not treat your GOUT with medication.2
WHAT CAUSES GOUT?
GOUT occurs when urate crystals build up in your joint due to high levels of uric acid in your blood. Your body produces uric acid when it breaks down purines which are substances that are found naturally in your body and found in certain foods.6
Normally, uric acid dissolves in your blood and passes through your kidneys into your urine but sometimes your body produces too much uric acid. This uric acid can build up, forming sharp, needle like urate crystals in a joint or surrounding tissue that can cause pain, inflammation and swelling.6
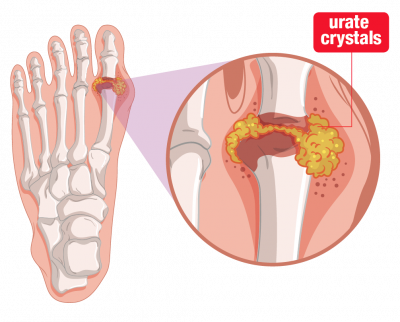
Uric acid crystals may also collect outside the joints and may even be seen under the skin, where they form small, firm, white lumps called tophi. Tophi are not usually painful however, they may break down and discharge fluid containing gritty white material – the uric acid crystals themselves. Uric acid crystals may also form in the kidney or other parts of the urinary tract, where they may occasionally impair kidney function or form kidney stones.2
WHAT FACTORS CAN PUT PEOPLE AT RISK OF DEVELOPING GOUT?
THERE ARE SEVERAL RISK FACTORS:2
•Men are more likely to develop GOUT than women
•GOUT usually develops during middle age in men and after menopause in women and although it is rare, younger people can also develop GOUT
•MEDICAL CONDITIONS:2,6
~ Type 2 diabetes
~ Chronic kidney disease
~ High blood pressure
~ High cholesterol
~ Underactive thyroid
•CERTAIN MEDICATIONS:2,7
~ Diuretics (water pills) that help your body get rid of salt and water
•LIFESTYLE FACTORS:2,6
~ Your diet:
– Eating too much food that is high in purines like meat and fish
– Consuming beverages sweetened with fruit sugar (fructose)
– Dehydration – not drinking enough water
– Consuming excessive amounts of alcohol regularly, especially beer
•OBESITY: 2,6
If you are overweight your body produces more uric acid and your kidneys have a more difficult time eliminating uric acid
•FAMILY HISTORY OFGOUT:2,6
If other members of your family have had GOUT, you’re more likely to develop the disease
•RECENT SURGERY OR TRAUMA:2
Surgery or trauma is also associated with an increased risk of developing GOUT
for more information on managing your Lifestyle on the Lifestyle tips page
THERE ARE SEVERAL RISK FACTORS:2
- Men are more likely to develop GOUT than women
- GOUT usually develops during middle age in men and after menopause in women and although it is rare, younger people can also develop GOUT
•MEDICAL CONDITIONS:2,6
~ Type 2 diabetes
~ Chronic kidney disease
~ High blood pressure
~ High cholesterol
~ Underactive thyroid
•CERTAIN MEDICATIONS:2,7
~ Diuretics (water pills) that help your body get rid of salt and water
•LIFESTYLE FACTORS:2,6
~ Your diet:
– Eating too much food that is high in purines like meat and fish
– Consuming beverages sweetened with fruit sugar (fructose)
– Dehydration – not drinking enough water
– Consuming excessive amounts of alcohol regularly, especially beer
•OBESITY: 2,6
If you are overweight your body produces more uric acid and your kidneys have a more difficult time eliminating uric acid
•FAMILY HISTORY OFGOUT:2,6
If other members of your family have had GOUT, you’re more likely to develop the disease
•RECENT SURGERY OR TRAUMA:2
Surgery or trauma is also associated with an increased risk of developing GOUT
for more information on managing your Lifestyle on the Lifestyle tips page

